Overview
Funded through PowerAmerica, the goal of this project was to design, fabricate and test a 135 kW automotive electric vehicle traction inverter using commercially available SiC power devices.
Method
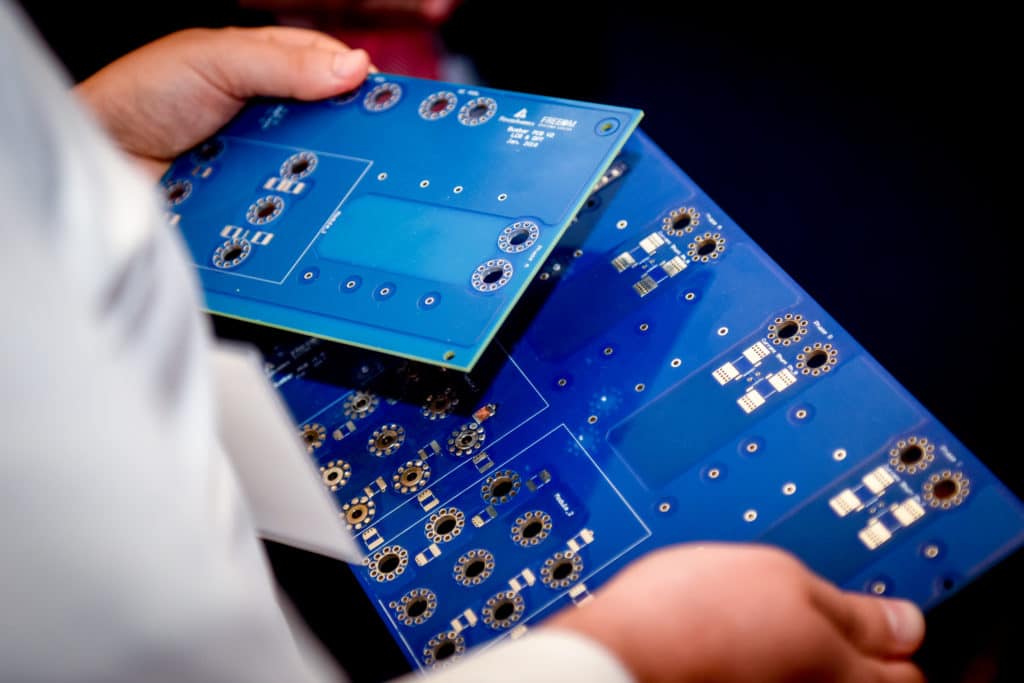
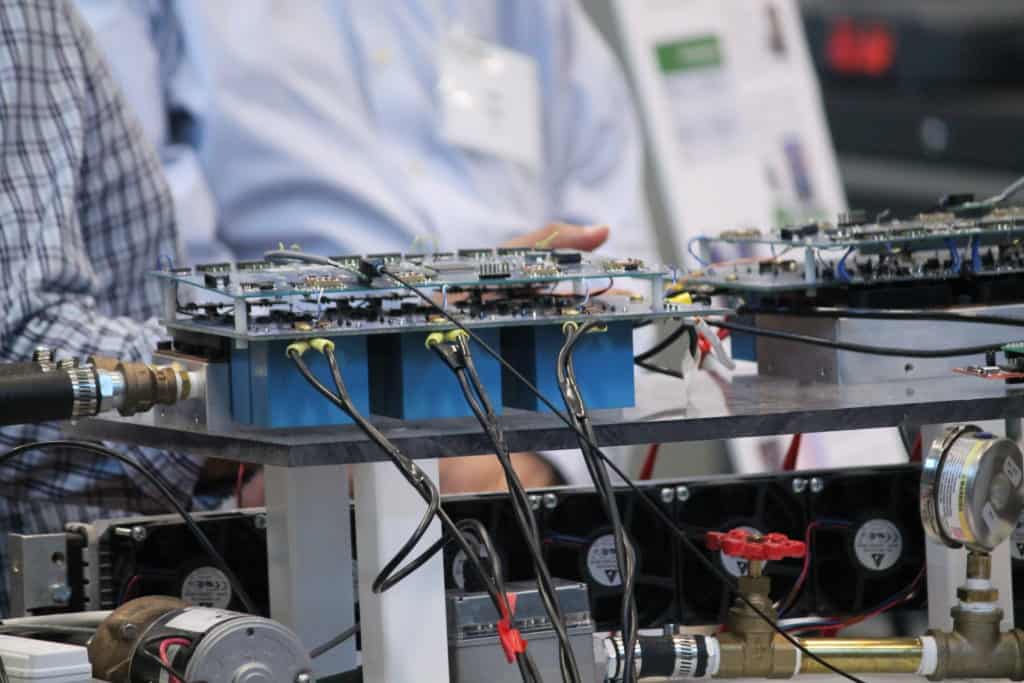
It used a two-stage topology with an interleaved-boost front end and three-phase voltage source inverter (VSI) connected by an adaptive 400 V to 1 kV DC bus. The planarized design with high-voltage and high-current PCB-based bus bar provides low parasitic power loop inductance.
Results
The end product has very high power density (19.3 kW/L, which includes the boost converter and VSI) and very high efficiency (99% peak). Overall system efficiency can also increase when coupled with a high-voltage electric machine. This improves the fuel economy of electric vehicles, thus extending vehicle range while reducing carbon emissions, which helps the auto industry meet aggressive corporate fuel economy requirements.
References
- B. Aberg, R. S. K. Moorthy, L. Yang, W. Yu and I. Husain, “Estimation and minimization of power loop inductance in 135 kW SiC traction inverter,” 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, 2018, pp. 1772-1777.
- R. Gao, L. Yang, W. Yu and I. Husain, “Gate driver design for a high power density EV/HEV traction drive using silicon carbide MOSFET six-pack power modules,” 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Cincinnati, OH, 2017, pp. 2546-2551.
- D. Rahman et al., “Design methodology for a planarized high power density EV/HEV traction drive using SiC power modules,” 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, 2016, pp. 1-7.